Attentional PointNet for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds
Anshul Paigwar, Ozgur Erkent, Christian Wolf and prof. Christian Laugier (INRIA - Team CHROMA)
|
Problem:
|
Nowadays, a large number of Automated Cyber-Physical Systems (ACPS) are based on probabilistic algorithms.
Validation of such systems is a crucial but complex task. |
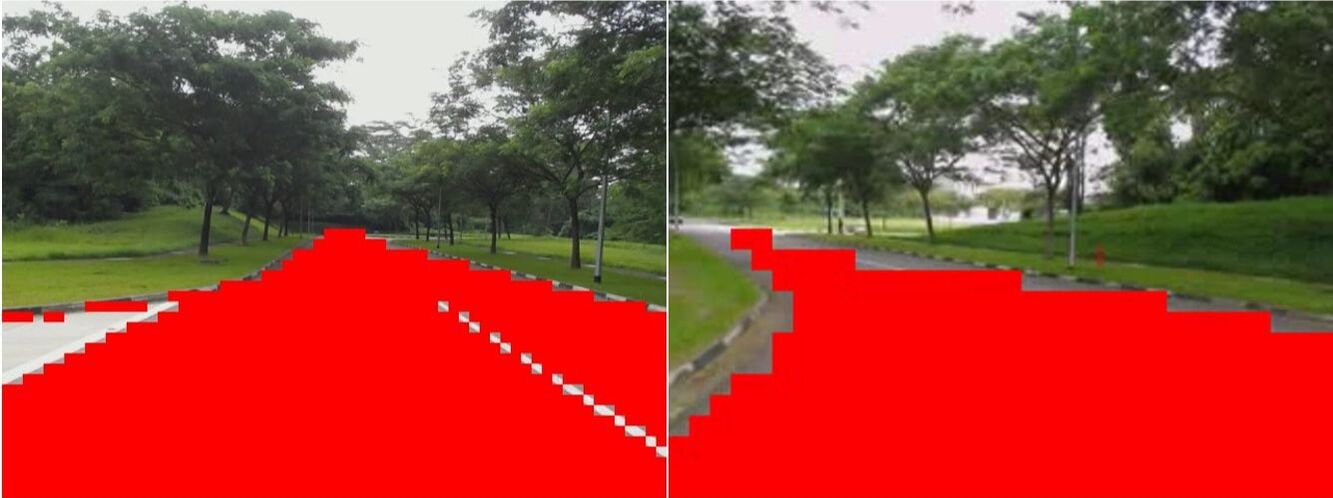
- In this work we validated CMCDOT, a probabilistic occupancy grid framework, developed at Inria, which also estimates risk of collision in near future.
- We use CARLA simulator to model the ego-vehicle and its sensors, as well as other vehicles in diverse intersection crossing scenarios.
- To validate the CMCDOT algorithm, we define appropriate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and create large number of simulations to evaluate the probability of meeting the defined KPIs. For the evaluation we use Plasma Lab, a statistical model checking platform.